This text is part of the Weather Preparedness & Resilience Toolbox developed by the YOUROPE Event Safety (YES) Group within YOUROPE’s 3F project (Future-Fit Festivals). It is aimed at everyone involved in planning, building, and operating open-air events. It helps festivals and other outdoor events become truly weather-ready by offering both practical and research-based resources as well as background information on weather and climate. Learn how to design safer and more weather-resilient outdoor events.
High winds & gusts
Medusa Festival, Cullera / Valencia, Spain -13 Aug 2022
Summary: Strong gusts hit the festival and parts of a main stage collapsed; one person was killed and dozens injured. Several temporary structures were damaged.
What went wrong: The gust front arrived during peak activity; either thresholds for suspending activity were not triggered in time, or structures were exposed beyond their safe wind ratings. Communication/evacuation took place but the structural failure timeline was too fast. Source: Reuters
Practical takeaway:
- Rely on near-real-time wind monitoring at structure height and predefine absolute wind gust limits for different structure types (e.g., small tents vs. main stage).
- Evacuation/stop criteria should be lower than the design collapse threshold to allow time for safe withdrawal.
Pohoda / Slovak festival tent collapse – July 2009 and 2024
Summary: Pohoda has experienced two major weather-related incidents: one in 2009 where a stage tent collapsed in a storm, resulting in one death and 52 injuries, and another in 2024 where a tent collapsed during a thunderstorm, injuring 29 people and causing the festival to be canceled.
The 2009 incident was followed by a protracted court case concerning the tent’s construction.
Source: spectator.sme.sk, IQ Magazine, 2024, The Guardian, 2009
Video link: YouTube.
What went wrong: Tent fixings and the protective decisions didn’t match the storm’s severity; anchoring and drainage can become critical when storms intensify. Quick decision and secure evacuation routes are essential.
Practical takeaway:
- For large temporary structures, require third-party structural checks and conservative operating wind limits; have contingency for rapid deconstruction or secure sheltering.
- Ensure routes can be quickly cleared and that crowd movement plans are tested for severe weather, evacuation/stop criteria should be lower than the design collapse threshold to allow time for safe withdrawal and should also consider severe rain as an alteration for anchoring calculations.

Image: A destroyed tent at Pohoda festival in Trenčín, western Slovakia, on July 13, 2024. (source: TASR quoted by spectator.sme.sk)
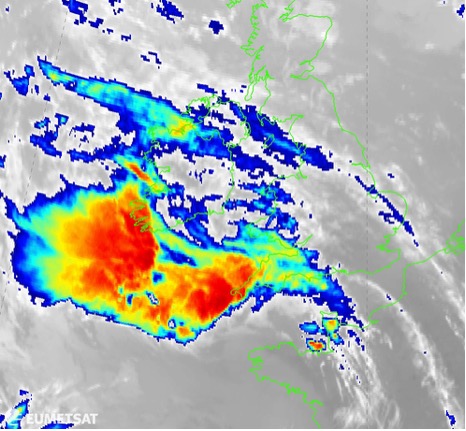
Image: Meteosat-10 infrared image of the storm over southern parts of the UK and Ireland, 17 July 2014 19:45 UTC. The infrared animation (18 July 00:00–07:00 UTC) shows how parts of the storm system grew in intensity and size, while others decayed. Source: user.eumetsat.int
Tropical storms / hurricanes in Europe
1) Storm Ophelia – Ireland/UK (Oct 2017)
Summary: Ophelia was a hurricane-origin system that reached the far eastern Atlantic and made landfall as an extra-tropical storm over Ireland on 16-17 Oct 2017, producing hurricane-force gusts (observed gusts up to ~156 km/h at Roche’s Point).
What went wrong: Unusual track and tropical origin increased public and operational surprise; exposed coastal infrastructure and events faced extreme wind and surge risk. Some event cancellations came late because the system’s tropical history led to uncertain expectations of intensity at higher latitudes. Source: Met Éireann
Immediate / required actions (Practical thresholds):
- Rapidly escalate to red warnings; cancel coastal/outdoor activities; secure temporary structures; prioritize road/venue closures and sheltering. The Guardian
- For tropical-origin systems approaching Europe, treat tropical-derived systems as high-impact even if extratropical transition is expected. Follow national Met Office/IPMA warnings and activate full high-wind closure protocols early. Met Éireann
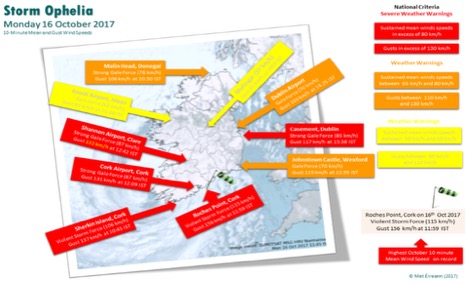

Image: Waves whipped up by Hurricane Ophelia crash over the seafront in Penzance on October 16, 2017 in Cornwall, England Photo by Matt Cardy/Getty Images quoted by IBT
2) Hurricane Lorenzo → Azores / NE Atlantic / Europe (Oct 2019)
Summary: Lorenzo became an eastern-Atlantic major hurricane and later transitioned/extratropical as it moved toward the Azores and NE Atlantic, producing severe winds, storm surge and large waves that disrupted ports, flights and island infrastructure.
What went wrong: Remote island event logistics (fuel, evacuation routes, transport) were stressed; maritime operations and coastal events were particularly vulnerable. Forecasts were available but operational impacts were large because of Lorenzo’s extreme size and swell. Source: Wikipedia
Practical thresholds:
- When storms threaten island/coastal venues, include contingency for fuel/evacuation, port closure protocols, and cancellation templates for marine/coastal events. Use marine warnings and wave forecasts as primary triggers.
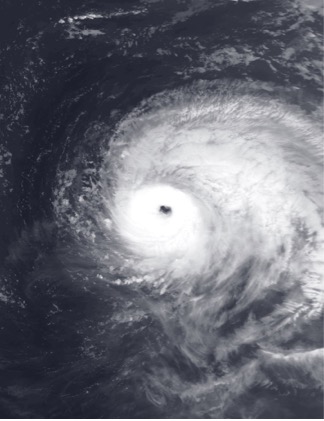
Image: Hurricane Lorenzo over the open Atlantic at 01:31 UTC on September 29, 2019. At the time, the National Hurricane Center analyzed the storm as having winds of 125 knots, making it a Category 4 hurricane. Wikipedia
3) Medicane Ianos (Sept 2020) Greece Mediterranean “tropical-like” cyclone
Summary: Ianos behaved like a tropical-type cyclone over the Mediterranean (a “medicane”), bringing torrential rain, high winds and floods across western/central Greece (landslides, inundation, infrastructure damage). Events and transport were disrupted and some areas declared states of emergency. Surce: ResearchGate
What went wrong: Medicanes are less common and can be underestimated; local flood/landslide vulnerability and limited shelter options in rural areas increased risk. Event plans often lack medicane-specific routing and sheltering. Source: MDPI
Toolbox takeaway:
- For Mediterranean events, add a “medicane contingency” to the plan: rapid shelter locations, landslide exposure maps, and pre-position rescue/medical contacts. Use local NOWCAST radar and satellite monitoring. Source: ResearchGate
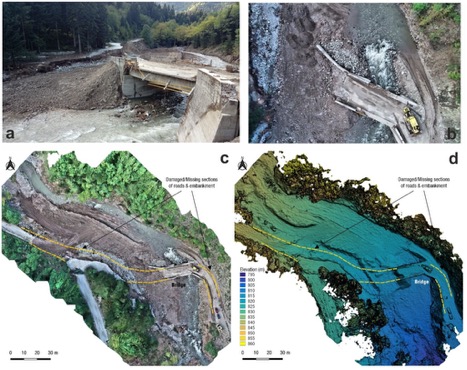
Image: Damaged bridge crossing of Karitsiotis River near Belokomiti. Ground (a) and vertical aerial (b) images of the damaged bridge undergoing repairs on 1 October 2020. UAS orthophoto (c) and digital surface model (d) of the Karitsiotis River bridge area (surveys 1 October 2020). Source: MDPI
Other incidents
- Indiana State Fair (country concert), USA, 2011: a gust front from a severe thunderstorm caused a stage roof collapse, killing seven and injuring dozens; this case continues to inform global festival wind and structural‑safety standards. https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Indiana_State_Fair_stage_collapse
- Lollapalooza, Argentina, 2018 – Lightning and a storm front damaged stage elements and broke a large screen; organisers cancelled an entire day after heavy rain flooded the venue, showing compound wind–rain impacts on temporary structures. https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Indiana_State_Fair_stage_collapse
- Various concerts worldwide, 2023 – Fox Weather documents multiple events where high winds and storms tore apart stages or site installations, injuring spectators and forcing evacuations or cancellations. https://www.foxweather.com/lifestyle/10-concerts-mother-nature-unwanted-cameo-2023-severe-weather
| Date | Event | Country | City / Site | Hazard Detail | Phase | Impact Type | Fatalities | Injuries | Operational Outcome | Notes |
| 2011-07-18 | Ottawa Bluesfest | Canada | Ottawa | Severe storm, wind gusts | Live | Main stage collapse | 0 | >10 | Show stopped, evacuation | Structural roof failure during performance |
| 2011-08-13 | Indiana State Fair Concert | USA | Indianapolis | Thunderstorm gusts | Live | Stage roof collapse | 7 | >50 | Event terminated | Benchmark case for wind thresholds |
| 2011-08-18 | Pukkelpop | Belgium | Hasselt | Thunderstorm, wind, hail | Live | Stages & tents collapsed | 5 | >100 | Festival cancelled | Multiple failures within minutes |
| 2012-06-16 | Radiohead Concert (build) | Canada | Toronto | Storm context reported | Build-up | Stage collapse | 1 | 3 | Concert cancelled | Crew fatality during build-up |
| 2019-07-19 | Tomorrowland – Freedom Stage | Belgium | Boom | Storm / strong winds | Live | Roof/ceiling failure | 0 | 0 | Stage closed | Structural damage between weekends |
| 2022-08-13 | Medusa Festival | Spain | Cullera | Strong winds | Live | Stage & structure collapse | 1 | >40 | Festival cancelled | Wind-driven debris fatality |
| 2024-05-22 | Political rally stage (ref. case) | Mexico | Monterrey | Thunderstorm winds | Live | Stage collapse | >5 | >50 | Event terminated | Key reference for temp. structures |
| 2024-07-13 | Pohoda Festival | Slovakia | Trenčín | Storm, wind, rain | Live | Tents & stages collapsed | 0 | >30 | Festival cancelled | Overnight storm damage |
