The Risk Management Circle in the Context of Events: 4 Risk Response
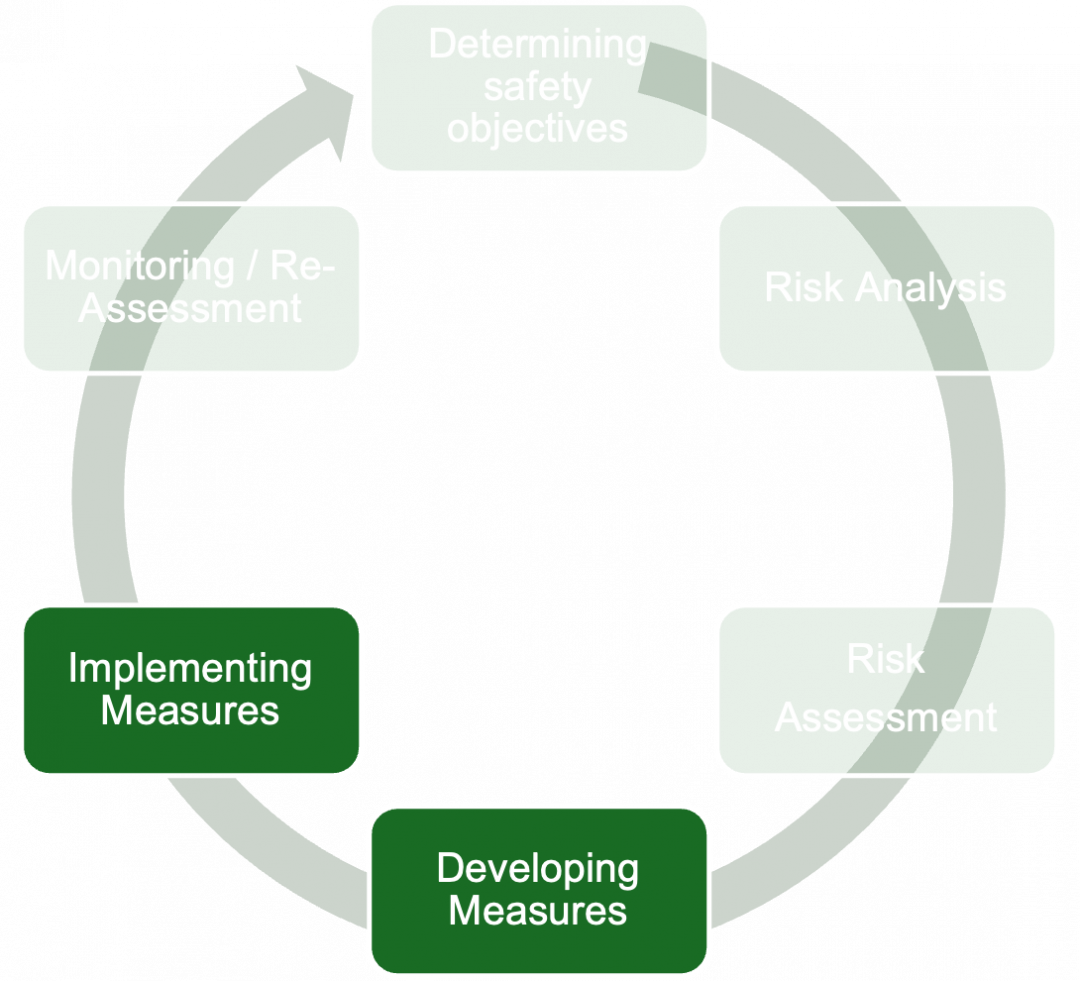
Risk Response is the phase of the risk management circle where strategies and measures are developed and implemented to reduce or eliminate the impact of identified risks. In event management, effective risk response ensures that potential threats are addressed proactively, safeguarding the event’s success.
Key Strategies for Risk Response
- Avoidance: Eliminate the risk entirely by changing plans. For example, if severe weather is a high-probability risk for an outdoor event, moving the event indoors can avoid the risk altogether.
- Mitigation: Implement measures to reduce the likelihood or impact of the risk. This can include technical solutions (e.g., backup generators to prevent power outages) or process changes (e.g., enhanced training for staff to reduce safety risks).
- Transfer: Shift the risk to another party. This is often done through insurance policies or outsourcing certain aspects of the event to third-party vendors. For instance, event insurance can cover financial losses due to unforeseen cancellations.
- Acceptance: Acknowledge the risk and prepare to deal with it if it occurs. This strategy is typically used for low-probability, low-impact risks where the cost of mitigation would outweigh the potential impact.
Implementation of Response Strategies
- Detailed Planning: Develop comprehensive plans that outline specific actions to mitigate each prioritized risk. Include detailed procedures and assign responsibilities to ensure clarity and accountability.
- Stakeholder Communication: Ensure all stakeholders are aware of the mitigation strategies and their roles in implementing them. Effective communication is crucial for coordinated risk management efforts.
- Training and Drills: Conduct training sessions and drills to prepare the event team for implementing mitigation measures. This can include emergency response drills, technical training, and scenario-based rehearsals.
- Technology and Tools: Utilize technology and tools to support mitigation efforts. This can include weather monitoring apps, security systems, and project management software to track and manage risks.
Examples of Risk Mitigation in Event Management
- Health and Safety: Implement stringent health and safety protocols, including first aid stations, emergency medical services, and clear signage. Ensure compliance with local health regulations to reduce the risk of accidents or health incidents.
- Technical Contingencies: Have backup systems in place for critical technical components. For example, use redundant internet connections and backup audio-visual equipment to ensure the event can continue smoothly in case of technical failures.
- Financial Safeguards: Secure event insurance to cover potential financial losses due to cancellations or other disruptions. This transfers the financial risk to the insurance provider, mitigating the impact on the event’s budget.


Risk Response is a proactive approach to managing potential threats in event planning. By developing and implementing strategies to avoid, mitigate, transfer, or accept risks, event organizers can safeguard their events against disruptions. Detailed planning, effective communication, and the use of technology are key components of successful risk mitigation. Risk mitigation can give rise to new risks or change existing ones. It is therefore necessary to assess the risks that could arise as a result of implementing the measures.
For example, a hazardous area could be shielded by a fence (technical measure). However, during the event, visitors climb on this fence to get a better view of the stage and fall off the fences and injure themselves. The measure must therefore be adapted, or another measure must be implemented.
______________________________________________________
Read all articles from this series on event safety:
Safety Planning for Events: An Introduction
The Risk Management Circle in the Context of Events: 1 Introduction
The Risk Management Circle in the Context of Events: 2 Risk Identification
The Risk Management Circle in the Context of Events: 3 Risk Assessment
The Risk Management Circle in the Context of Events: 4 Risk Response
The Risk Management Circle in the Context of Events: 5 Risk Monitoring and Review
The Risk Management Circle in the Context of Events: 6 Risk Mitigation
Crowd management: 1 An Introduction
Crowd Management: 2 The need of a systematic approach
Crowd Management: 3 The people
Crowd Management: 4 Safety by Design
Crowd Management: 5 The Ingress and Egress Areas
Emergency planning: Introduction
Emergency Management: 1 Emergency Plans
Emergency Management: 2 Scenarios
Emergency Management: 3 Learning from Disasters
